EXAM-2 (100 points), General Genetics pcb3063-01, su99, HW Bass, 18 June 1999
KEY
Section I (26 points) VOCABULARY & DEFINITIONS
Section II (24 points) MULTIPLE CHOICE
Section III (26 points) SHORT PROBLEMS
Section IV (24 points) LONG PROBLEMS
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
TOTAL (100 PT.)
bonus (2 points)
EXAM 2 GRADE
CLASS AVERAGE
CLASS RANGE
HONOR CODE
(must be signed to receive grade)"I did not give or receive help on this exam"
Name (written) _______________________
Student ID # _______________________
Signature _______________________
Date _______________________
Section I VOCABULARY AND DEFINITIONS (26 points)
VOCABULARY (14 pt., 2 pt. each), fill in the blanks
1 Mating a heterozygous individual with a recessive homozygote is called a _TEST CROSS__.
2 The physical exchange of segments between homologous chromosomes is called _RECOMBINATION_.
3 A genotype in which the mutant linked alleles in a double heterozygote are present on opposite homologous chromosomes is said to have the __TRANS__ configuration
4 On a genetic linkage map, 1 map unit is equal to __1 % RECOMBINATION (OR 1 centiMorgan)_.
5 The observed number of double recombinants divided by the expected number is the __COEFFICIENT OF COINCIDENCE_.
6 The inactivated X chromosome can be seen as a densely staining nuclear structure called a __BARR BODY__.
7 The NOR locus is the site of the _LARGE rDNA (or large ribosomal RNA)___ genes.
DEFINITIONS (12 pt., 3 pt. each)
Give brief, less than 30 word definitions for each
8 sex-linked trait (define and give one example)
An X-linked trait, derived from a gene located on the X chromosome, one of the sex chromosomes.
examples: color blindness, hemophilia A and B, Hunter syndrome, Fargy's disease, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, Duchenne Muscular dystrophy. [not hen feathering, not pattern baldness]
9 hypomorph (define and give one example, real or made up)
An allele in which the gene is less active or gene product less abundant than the wild-type allele.
eg) AA = 100 %, aa = 70%
[NOT AA = 100% and Aa = 50% - that is partial dominance]
[NOT AA = red, Aa = pink, aa = white - that is " " ]
[NOT a affects expression of gene b]
10 aneuploidy (define and give one example)
A variation in chromosome number in which an individual has a total chromosome number of something other than a multiple of the haploid set, as with trisomy or monosomy
eg) trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome), Patau Syndrome, Edward Syndrome
11 metafemale
A drosophila superfemale, resulting in a condition where the ratio of X chromosomes to the sets of autosomes exceeds 1.0
Section II (24 points, 3 pt. each) MULTIPLE CHOICE
1 In crossing over
A. Genetic exchange occurs before chromosome replication
B. The probability of its occurrence decreases with increasing distance between the genes exchanged
C. Occurs between two loci very close together
D.
The reciprocal exchange between homologous chromosomes occurs
2 The genes in order ho - dp - da have the following map distances. Genes ho and dp are 9.0 map units apart, and genes dp and da are 26.3 map units apart. What is the probability of a double crossover in these regions? (may need to round off your answer)
A. 1.3%
B.
2.4%C. 3.4%
D. 4.5%
E. 5.6%
3 Which of the statements below regarding X-linked inheritance of a recessive trait is FALSE?
A. Heterozygous females will transmit each X-linked allele to about half of their daughters
B. Males inheriting an X-linked allele have the trait
C.
The trait would be more common in femalesD. Heterozygous females will not display the trait
E. Hemophilia A is an example of an X-linked trait
4 The basic diploid chromosome number in Chrysanthemum is 18. A new species of Chrysanthemum is found that has four complete sets of the chromosomes found in the 18-chromosome species. This species is said to be
A. Polyploid [1 pt for answer of A only]
B. Diploid
C. Pentaploid
D. Tetraploid [1 pt for answer of B only]
E
. Both A and D
5 47, XXY is a condition known as
A. Trisomy-X syndrome
B
. Klinefelter syndromeC. Turner syndrome
D. Double-Y syndrome
E. Fragile X syndrome
6 The main problem with inversions occurs when
A. One of the inverted fragments is spontaneously lost
B. Pairing in mitosis occurs
C. The inversion is a homozygous condition
D. There is no problem
E
. The paired chromosomes undergo crossing-over in the region of the inversion
7 An organism
A. Cannot tolerate any form of a deletion or duplication
B. Is never affected by changes in gene dosage
C. Can usually tolerate large chromosomal duplications or deletions
D
. Can often tolerate a small chromosomal duplication or deletionE. Both B and C
8 Maternal inheritance refers to traits that
A. Are all X-linked
B. Follow Mendelian segregation
C. Are encoded by nuclear genes [this is maternal affect]
D. Are transmitted only through maternal cytoplasm
E. None of the above
Section III (26 points) SHORT PROBLEMS
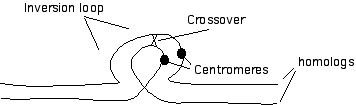
9. (8 pt) Draw an inversion heterozygote at synspsis in which the centromere and a crossover is located within the inverted region. Label all structures.

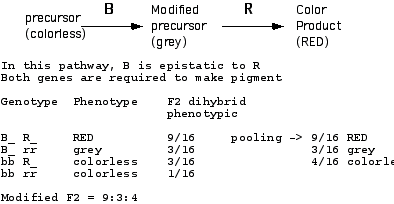
10 (10 pt) Draw out and label a any pathway in which two genes (B and R) interact such that B is epistatic to R. Label the phenotype of the the precursors and final products, and indicate the F2 phenotypic ratios that would result from a dihybrid cross
11 (8 pt) Two-point testcrosses revealed the following map results:
p___________s = 9 map units
p___________b = 14 map units
A. What are the two possible maps for these loci?
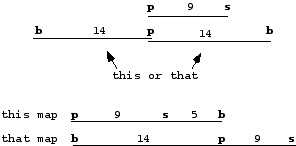
B. Assuming the availability of genetics stocks with dominant and recessive alleles for these genes, What cross would resolve the two possible maps?
the test cross: SsBb x ssbb
Section IV (24 points) LONG PROBLEMS
You carry out a three point mapping experiment for three linked loci in Drosophila. Each locus has recessive alleles which in the homozygous state produce purple head flies (ph), twitchie winged (tw), or clear eyes (ce). A triple mutant was crossed with a wild-type fly to create a triple heterozyogous fly named Pete (phenotypically wild type). Pete was used in a three point test cross with a triple mutant tester named mutabeulonia (ph/ph, tw/tw, ce/ce). You worked all weekend scoring the 10,000 progeny before they could get away and into your coffee, and found the following results.
Determine and draw the genetic map (assuming no interference).
3800 normal flies
396 twitchie winged flies
396 purple headed, clear eyed flies
3800 twictchie winged, purple headed, clear eyed flies
796 twitchie winged, clear eyed flies
8 clear eyed flies
8 twitchie winged, purple headed flies
796 purple headed flies
Be sure to name the different classes and indicate gene order and map distances.
(MUST SHOW YOUR WORK FOR CREDIT).
ph ----------------------- ce ------------ tw
16.06 8.06
(15.9 + 0.16) (7.9 + 0.16)
______________________________________________________
genotype number class percent
------------------------------------------------------
+ + + 3800 NCO
76% NCO
ph ce tw 3800 NCO
------------------------------------------------------
+ ce tw 796 SCO
15.9% SCO between ph and ce
ph + + 796 SCO
------------------------------------------------------
+ + tw 396 SCO
7.9% SCO between ce and tw
ph ce + 396 SCO
------------------------------------------------------
+ ce + 8 DCO
0.16 % DCO
ph + tw 8 DCO
------------------------------------------------------
Bonus (2 pt) draw a 4 strand crossover -
![]()